计算机系统I-处理器基本原理
The Processor: Basic Principles
What is the architecture of computers
Von Neumann structure: data and programs are in memory.
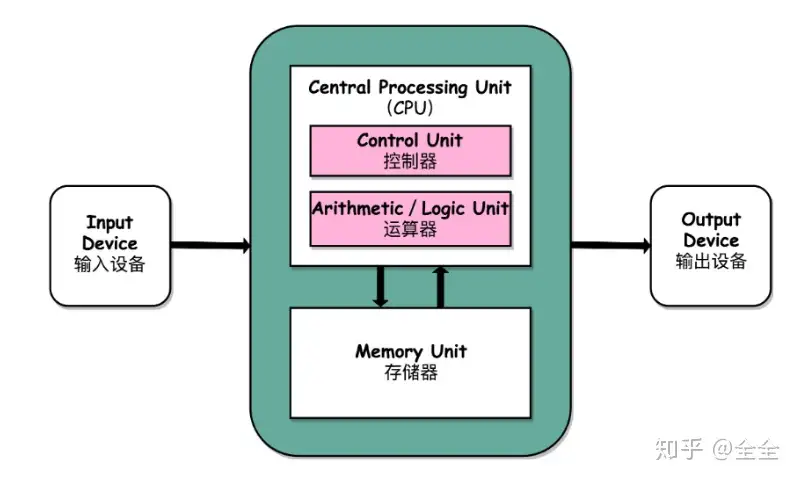
What is the inside of Processor (CPU)
- Datapath: performs operations on data
- Control: sequences datapath, memory, …
- Cache memory
- Small fast SRAM memory for immediate access to data
How to use CPU to solve problems
Design methodology 1: Common digital system
Finite state machine (FSM)
graph LR
A[input]
A -->B[Combinational circuit
Status transmission conditions]
A -->C[Combinational circuit
Output processing]
D[State storage] -->B
C-->E[Output]
B-->D
B-->C
Design methodology 2: Control of Register Transfers
Control of Register Transfers
Register transfers performed on registers control that supervises the sequencing of the register transfers.
Design methodology 3: Control of Register Transfers
General system: Program state machine (PSM)
Turing Machine
Basic idea
- Use machine to simulate mathematical computation process of humans by paper and pen.
- Two simple operations
- Write or delete a symbol from the paper
- Move the attention from one position to another of the paper
- The next operation depends on
- the symbol in one position of the paper that the person pays attention to
- the thinking state of the person currently
- Turing constructs an ideal machine
Components of Turing Machine
- An infinitely long paper tape TAPE
- A read/write head HEAD
- A set of control rules TABLE
- A state register
Instruction structure of Turing Machine
, where are all finite sets
- Q is the state set
- is the input alphabet, which does not include the special empty " ";
- is the alphabet, where is the empty, and
- is the transfer function: , where L and R represent the read/write head moves left and right, respectively
- q0Q is the beginning state
- qaccept is the accept state
- qreject is the reject state, and qrejectqaccept
Program of Turing Machine
- is the current state of the machine
- is the symbol read by the machine
- is the symbol waiting to be written to replace
- R, L, N represent moving right one step, moving left one step, or remain static
- is the next state of the machine
Practical Turing Machine – A Real Computer
A large enough storage to replace the tape
- Magnetic storage for replacement
- Semiconductor storage for replacement
Storing the inner state
- Inner state does not store immediate, downgrading the efficiency
- Register to store the immediate
- Can significantly simplify computational structure and improve computing efficiency
Enhance the processing capability of HEAD–CPU
- Require a stronger HEAD
- Can be implement by Control of Register Transfer Technique: CPU
- Satisfactory Universal Turing Machine
CPU
Logics in CPU
Unlocked vs. Clocked
Clocks used in synchronous logic

Performance
Being able to gauge the relative performance of a computer is an important but tricky task. There are a lot factors that can affect performance
- Architecture
- Hardware implementation of the architecture
- Compiler for the architecture
- Operating system
Furthermore, we need to be able to define a measure of performance
- Single users on a PC -> a minimization of response time
- Large data -> a maximization of throughput
Response Time and Throughput
- Latency (Response time)
- is the time between the start and completion of an event
- How long it takes to do a task
- Throughput (bandwidth)
- is the total amount of work done in a given period of time
- Total work done per unit time
How are response time and throughput affected by
- Replacing the processor in a computer with a faster processor
- Adding more processors?
Measuring Execution Time
Elapsed time
- Total response time, including all aspects
- Determines system performance
CPU time
- Time spent processing a given job
- Comprises user CPU time and system CPU time
- Different programs are affected differently by CPU and system performance
How can computers run fast
The main goal of architecture improvement is to improve the performance of the system.
- Describe a thing with the least instructions – Algorithms, compiling
- Do more things in a Clock cycle – Architecture
- Increase the speed of “core” – Main frequency
CPU Clocking
Operation of digital hardware governed by a constant-rate clock
- Clock period: duration of a clock cycle
e.g., 250ps = 0.25ns = - Clock frequency (rate): cycles per second
e.g., 4.0GHz = 4000MHz = Hz